Retail fulfillment is a complete process from receiving an order until delivering it to the customer. According to a recent report, the global eCommerce fulfillment market is expected to grow with a CAGR of 13.12% from 2023–2030.
Given the rising trend of online shopping, retailers need to integrate automated, customer-focused, and data-backed retail fulfillment into their core capabilities to stay competitive. Those strategies can help improve customer experience, facilitate efficient inventory management, and drive sales for your business.
In this guide, we’ll provide a comprehensive understanding of fulfillment benefits, its processes and strategies, and the most common retail fulfillment models for your optimal operations.
What is retail fulfillment?
Fulfillment meaning in retail is a process including receiving, processing, and delivering orders from merchants to customers.
Nowadays, most retail activities and successes depend on efficient processes and strategies. Many shops are finding it hard to meet the rising demands of their customers regarding value, convenience, and quick delivery. The ability to adjust to changes in the business environment and having the right resources on hand will be essential to your long-term success.
How does fulfillment benefit retail stores?

Improved customer satisfaction
Customers expect to receive their orders accurately and on time, so retailers should implement an effective retail order fulfillment process. Efficient retail fulfillment helps minimize delivery time, ensure accuracy of goods delivered, and maintain transparency. Customers are more likely to come back for a second purchase if they’re satisfied with their first transaction. That, in turn, can improve customer loyalty and help your business thrive.
Optimized inventory management
The retail fulfillment process empowers retailers with effective inventory management. Efficient retail fulfillment helps retail managers frequently control inventory levels and precisely forecast demand to ensure they have enough stocks to meet customer’s needs.
Adaptation to consumer preferences
Consumer shopping habits are changing over time, which retailers should be aware of and adapt their fulfillment process accordingly. Businesses can use a variety of fulfillment strategies, such as in-store pickups, dropshipping or subscription services, to better meet customer expectations and stay competitive.
Enhanced operational efficiency and increased profit
Fulfillment operations can impact significantly on the overall performance of your business. By making sure that your orders are processed and delivered effectively, you can reduce picking costs by a half like Walmart, enhance customer satisfaction, boost sales and profits.
What is a fulfillment process in retail?
Generally, there are five steps in a fulfillment process in retail. Follow us to see how it works.
Step 1: Receive inventory from suppliers
As soon as the package arrives at your receiving location, verify its accuracy. Then, check carefully to see if the following components match your PO:
- Product quantities
- Product details: size, color, price, etc.
- SKU numbers
If you detect a mistake with inventory, contact your suppliers right away. They’ll cooperate with you to fix any errors, regarding faulty products, wrong products received, or missing numbers of items. The sooner the better.
Lastly, after confirming that you received the right inventory and quantity, it’s time to store them in your warehouses or distribution centers.
Step 2: Store inventory in warehouses

Scan barcodes and enter SKU numbers for items as soon as they arrive in your inventory management system. After that, use a pallet, bin, or shelf to place the goods in storage for easy pickup later.
Tracking things when they leave your warehouse is just as crucial as tracking them when they arrive since they’re parts of the order cycle.
To ensure having enough inventory for fulfillment, you should know when, what, and how much to reorder from your suppliers. While you can use spreadsheets to track stock flow, an inventory and purchasing system can notify you when it’s time for replenishment and auto-replenish products. This will save you a lot of management time for more important tasks like sales or marketing to increase revenues.
Step 3: Pick and pack
The next stage in fulfillment retail after receiving an online order is to pick and package the products for delivery.
It’s a crucial phase in your fulfillment operations since you want your orders to remain intact and arrive at your customer’s place securely.
There are some points to consider in this step:
Plan a picking route
The ultimate purpose of this point is to save time for you and your pickers. According to research, traveling accounts for 55% of the total order-picking time. Therefore, you should take into consideration the size and layout of the warehouse, the type and volume of inventory in order to figure out the most optimal picking routes.
Scan by barcode
Barcode scanning helps improve your warehouse efficiency by automating tasks like receiving, picking, and shipping and increase accuracy by minimizing the risk of human errors. Also, barcode scanning software can recommend efficient picking routes for each warehouse employee.
Double check the products picked
This may seem obvious, but retailers should pay attention to every detail in the packaging step to guarantee the product is correctly labeled and securely wrapped.
Use appropriate packing materials
Your choice of packaging materials really matters as it helps protect your products during delivery, promotes your brand image, reduces your shipping costs, etc. Some important criteria to choose the suitable materials include:
- Secure and durable
- Cost-effective
- Easy to use
- Widely available
- Environment-friendly and legally compliant
Step 4: Ship orders
Now, your online orders are ready for delivery. Depending on your applied fulfillment model, shipping will appear different.
If you run a small business out of your home, for instance, you might schedule a carrier pickup or hand the package to the post office for delivery.
Step 5: Process eCommerce returns
Returns have reached 16.5% in 2023, amounted to over $231 billion in returned merchandise.
When a client returns the product to the distributor, this is known as reverse logistics. Reverse logistics consists of exchanges, refunds, and even rubbish to be disposed of, reused or recycled.
The general process of handling returns is as followed:
- Inspect the returned items: Make sure you note any damage found on the objects.
- Record return and inventory: You must record the return in your system and add the item back to your stock if you can refill and resell it later. If it’s damaged or not sellable, you need to have a plan in place on how to get rid of it.
- Satisfy customers: Based on your return policy, you may need to give customers another item, provide them with store credits, gift cards as replacement, or refund them in cash or via bank transfer.
The following figure and insight may surprise you. 81% of online shoppers returned their purchases because of damages or defects. Other reasons include:
- Item doesn’t fit.
- Item mismatches description.
- Customers don’t like the items.
- Customers ordered multiple items/sizes.
- Items arrived late.
You can manage return process and lower your return rate with these best practices:
- Pack the goods safely
- Provide thorough size charts
- Optimize product descriptions
- Improve item photos
- Deliver products on time
What are retail fulfillment models?

It’s essential for retailers to know the available options of retail fulfillment and how each model aligns to your business.
In general, there are 4 major order fulfillment models that are widely adopted in the retail industry. In this section, we’ll illustrate these 4 options by comparing their main features, pros and cons, and whether it’s suitable for your business.
Third-party logistics (3PL)
A third-party logistics company receives shipments of goods, monitors warehouse stock levels, chooses and packages orders, and ships them to your customers. Other names for a 3PL include retail fulfillment centers, fulfillment warehouses, and fulfillment companies.
Typically, 3PL providers offer the following services:
- Warehousing
- Inventory management
- Picking and packing
- Shipping and receiving returns
Some extra services are also provided:
- FTL and LTL freight shipping
- Freight forwarding
- Kitting
- Reverse logistics
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
When to use:
3PL is suitable when you plan to expand your business without intending to build and manage your own warehouse. Moreover, if your business often experiences sales seasonality or industry fluctuation, you may also opt for a 3PL service to take care of your fulfillment process.
Self-fulfillment
When retailers fulfill orders by themselves without help from a third-party logistics provider, it’s called self-fulfillment.
In this case, you’ll need a system to initiate and manage the retail fulfillment process.Here’s how the procedure works.
- Receive an order
- Select appropriate packing materials
- Package an order
- Label the order and deliver
- Follow the package to its intended location
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
When to use:
Self-fulfillment could be more economical if your business is small and just getting started. It’s suitable when you have enough resources to support your internal logistics, and you want to have more control over your brand and consumer satisfaction.
Dropshipping

Dropshipping is a model of selling goods online without having to keep them in stock. When customers make an order, the seller sends information to the supplier’s system. The supplier subsequently takes care of order fulfillment and ships the product to the consumer.
Indeed, sellers, or dropshipping providers, serve as an intermediary and concentrate on product promotion and sales.
The dropshipping process includes the following major activities:
- Packing and shipping
- Inventory management
- Customer experience management
- Customer communications
As your supplier mainly takes charge of the order fulfillment procedures, retaining customer loyalty should be your focus now.
Every dropship order involves these five steps:
- Step 1: You sign an agreement with a manufacturer, retailer or wholesaler to provide the goods you advertise.
- Step 2: Customers place orders via your website, apps, marketplaces, etc.
- Step 3: You notify your suppliers of the orders.
- Step 4: The suppliers select, package, and send the products to your customers.
- Step 5: You pay your suppliers.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
When to use:
Briefly, dropshipping is the practice between vendors and suppliers to sell and fulfill orders while in fact, vendors or sellers don’t keep the items in stock. Therefore, startups and businesses with new product testing can benefit from this strategy.
In-store pickup

In-store pickup or buy online, pick up in store (BOPIS) means customers can purchase items online and pick them up at a physical place. As a result, this strategy helps retailers save shipping fees, increase store traffic, and boost sales. In 2022, there were 47% of U.S. customers buying more products when they visited the store.
By streamlining online to offline retailing with in-store pickup, retailers can engage with customers in person and offer them a more comfortable shopping experience. BOPIS or click and collect gained enormous popularity during the COVID-19 pandemic, and now 54% of retailers have offered it.
Below is how the procedure works:
- Step 1: Customers shop online.
- Step 2: Retailers prepare the orders.
- Step 3: Customers pick up their orders at the chosen physical stores.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
When to use:
In-store pickup is suitable if you’re operating both online and offline, and want to minimize both shipping expenses and cart abandonment. Then, higher store traffic can convert into higher revenue from extra items sold.
4 retail fulfillment strategies to optimize the process

Fulfillment optimization is all about making sure that products get from the warehouse to customers as smoothly and quickly as possible. Let’s explore some factors to enhance your fulfillment process below:
Optimize warehouse layout
How you organize your warehouse can greatly impact your fulfillment operations. Optimal warehouse layout design can reduce travel times and improve accuracy during picking and packing steps
There are 3 most used warehouse layouts:
- U-shaped
This warehouse layout is in the form of a “U”, or a semicircle. Receiving and shipping are next to each other on two ends of the “U” and storage is located at the back of the warehouse.
This design works well for small warehouses, but note that congestions may occur if the receiving bay is too close to the shipping bay.
- I-shaped
In the shape of a straight line, this layout has shipping and receiving on two ends, while storage is in the middle. This design is helpful when your warehouse has to deal with high-volume orders because all goods will move in the same single direction to reduce travel time.
- L-shaped
This layout is in the shape of an “L” or a 90-degree angle. With storage being in the corner, shipping and receiving bays are located at each end of the “L”.
L-shaped warehouses work well for businesses that operate cross-dock or swiftly move goods from an inbound truck to an outbound truck.
Focus on staff training
Fulfillment staff training is important to ensure accuracy, safety, and productivity. As a retail manager, the following are best practices in training your fulfillment employees:
- Provide detailed instructions on each task, such as how to operate equipment, pack orders, handle inventory, and label shipments
- Emphasize the importance of accuracy and speed in fulfilling an order, encourage your employees to stay adaptable to changing demands
- Familiarize your staff with the use of technology in the fulfillment process, such as how to use the warehouse management system (WMS), robots, scanners, etc.
- Conduct regular assessments to control your staff’s performance and encourage improvement
Regularly monitor fulfillment performance
It’s crucial to regularly assess how well you’re fulfilling your orders. This could help you determine where enhancements might be implemented and guarantee that your fulfillment processes are satisfying your customer requirements.
Some key metrics used in evaluating fulfillment performance includes:
- Total order cycle time
- Order picking accuracy
- Order fill rate
- Rate of returns
- Shipping cost per order
Invest in technology
Technology can facilitate inventory level tracking, communication improvement, and process automation.
Warehouse management system (WMS)
A warehouse management system is a retail fulfillment solution that assists businesses in managing day-to-day operations in the warehouse, from the time materials and items arrive at a fulfillment or distribution center until they depart.
Key features of a WMS include:
- Real-time data sync
- Customization with low to no code
- Continuous order processing
- Optimized inventory management
- Performance analytics and reports
Best warehouse management software:
- Easyship
- ShipHero
- Oracle Warehouse Management
- Veeqo Inventory and Fulfillment
Order fulfillment software
Magestore Order Fulfillment is exclusively made for Magento businesses handling multiple orders per day to automate and optimize the order processing. The fulfillment module supports the typical order fulfillment process at an SME warehouse below.
- Verify order (optional): Sales staff confirm and edit customer’s shipping and billing address.
- Check available stock: Separate orders into 2 groups whether all ordered items are in stock or not
- Pick items: Print picking list for multiple orders at once, scan a barcode to verify picked items
- Pack items: Create multiple packages for an order, print and add packing slips
- Deliver packages: Display shipping information and tracking number provided by the carrier
Shipping software system
Shipping software is a management solution to automate and simplify the product shipment.
Key features to evaluate a shipping software include:
- Order tracking and management
- Label printing and packaging
- Shipping rate calculation
- Carrier selection
- Tracking shipment in real time and notifications
Top shipping management software:
- ShippingEasy
- ShipMonk
- Ordoro
- ComFreight
Returns management system (RMS)
A returns management system (RMS) is retail fulfillment software designed to assist eCommerce companies in streamlining and automating the product returns.
Key features of a RMS include:
- Automated customer communications
- Disposition management for resale opportunities and cost recovery
- In-depth returns merchandise authorization (RMA) management
Top RMS to consider:
- AfterShip
- Samsara
- Ordoro
- ShippyPro
FAQs
What are 4 types of fulfillment?
These 4 types of fulfillment include:
- In-house fulfillment: You’ll take full control over the order fulfillment, from receiving, storing inventory to delivering to customers.
- Outsourced fulfillment: If you choose this option, a third party will do all fulfillment-related tasks, including receiving inventory and storing it. They also help select, package, and send out the products.
- Dropshipping: Dropshipping and outsourcing are comparable, however, dropshipping eliminates the need for inventory management. Retailers don’t hold products in their stock. Rather, they’ll request the ordered products from the suppliers. After that, it’s the suppliers who take charge of delivering the products to the customers.
- Hybrid fulfillment: This approach is a combination of some order fulfillment types listed above. For example, a business might use dropshipping for non-custom items while processing orders for custom items or items that need to be assembled before shipping in-house.
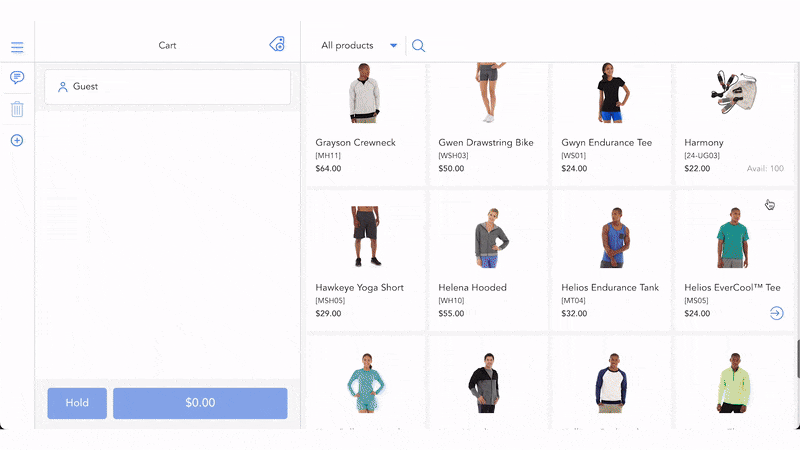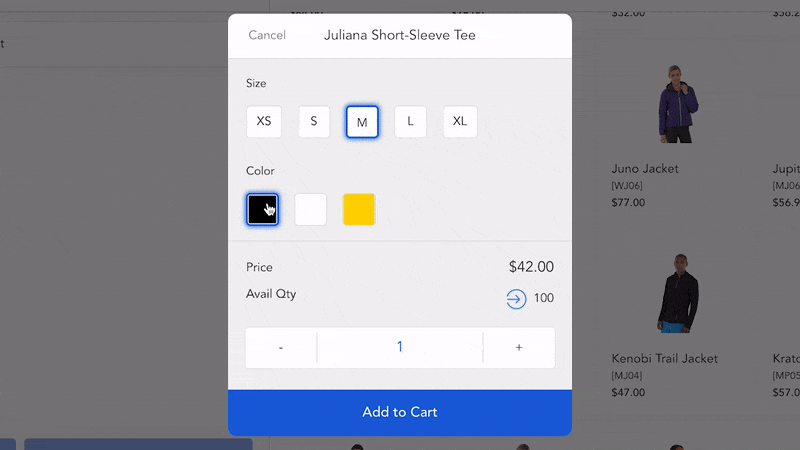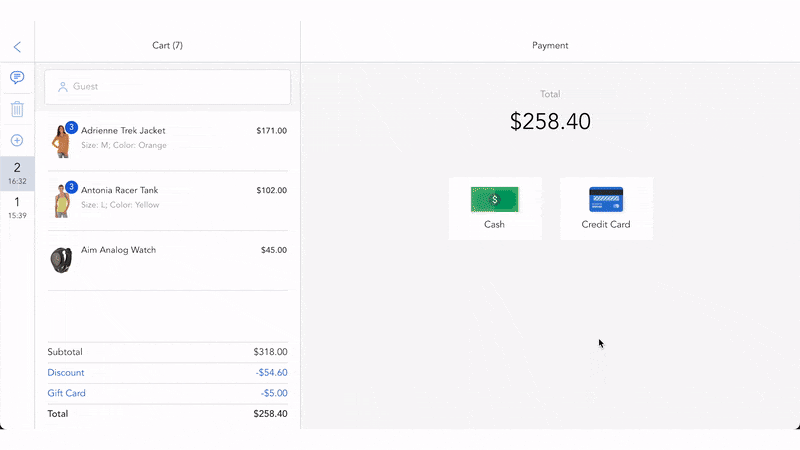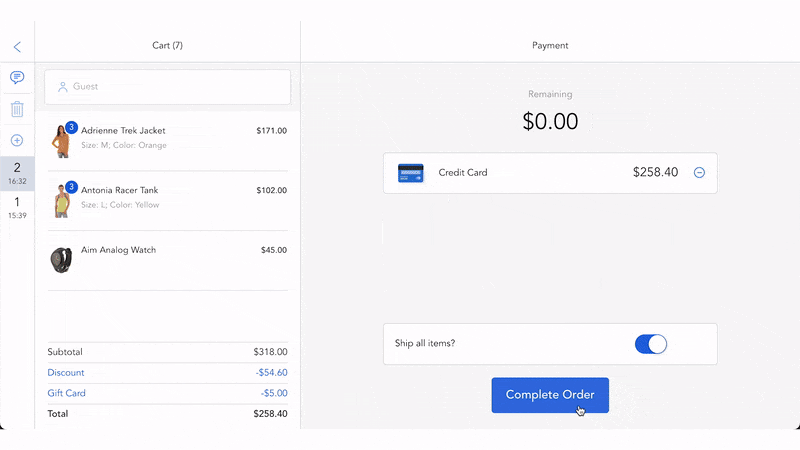
What is fulfillment in Retail POS?
Retail point of sale (POS) software is a technological solution that helps checkout products to complete sales, process returns, track order history, manage retail operations like inventory control, employee management, etc.
Retail POS software facilitates fulfillment process in the following ways:
- Automate order fulfillment
- Reduce shipping costs by suggesting the best time and cost-saving delivery options
- Support managing multiple warehouses and store locations
- Better control your inventory with real-time data sync between your warehouses, eCommerce site, and the POS system
What’s the difference between retail fulfillment and B2B fulfillment?
B2B fulfillment is simply shipping bulk orders from one business to another. This could mean sending products to a retail store, or to a corporate office for employees to use.
On the other hand, retail fulfillment involves packaging and shipping orders from retailers directly to customers or a specific retailer.









A Complete Guide on Optimization Strategies’ is a treasure trove of insights! The comprehensive guide provides invaluable tips for businesses seeking to enhance efficiency. Thanks for simplifying the complexities of retail fulfillment!
Inventory used to be a nightmare before we got planogram software. Now we know immediately when stocks are plummeting and how to make sure we’re avoiding backorders.