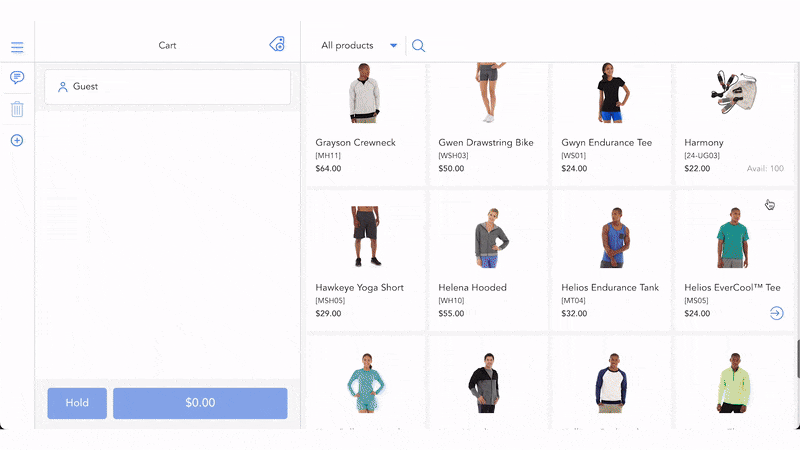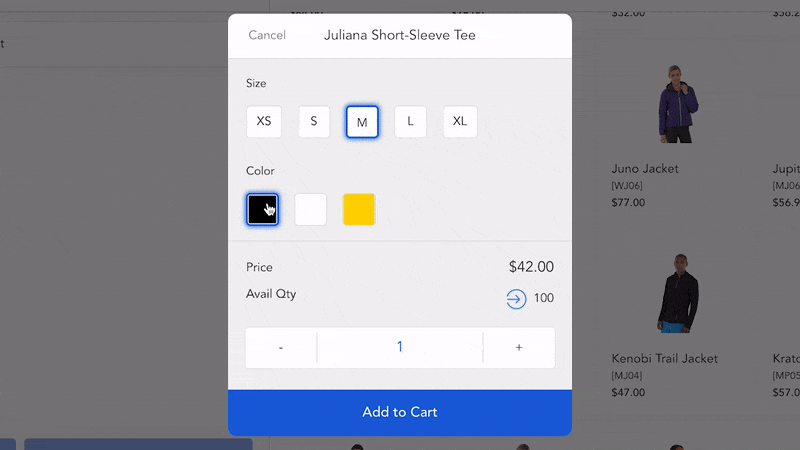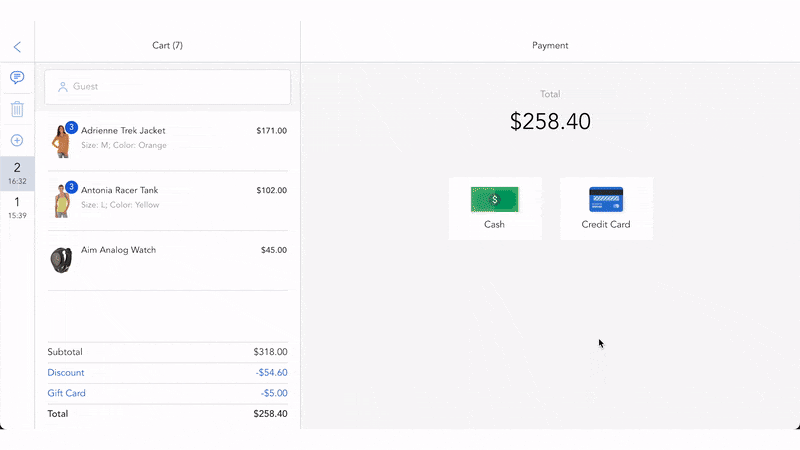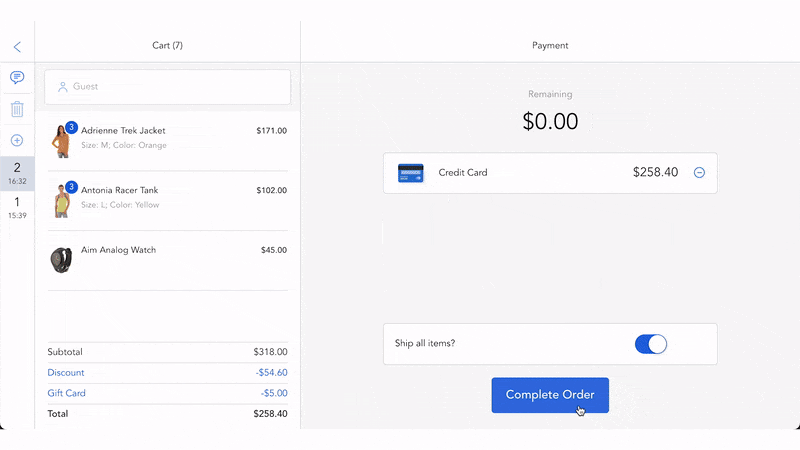
According to the 2025 AFP Payments Fraud and Control Survey, up to 79% of organizations experienced payment fraud attacks in 2024. In this increasingly complex situation, payment tokenization has become an effective solution to help merchants retain their customers’ trust and meet the industry security standards.
Tokenization in payments transforms sensitive cardholder data into randomly generated tokens that can’t be reversed to obtain real payment information. Incorporating this security technology into your business empowers you to safeguard your customers’ card details from fraudsters or hackers, thus strengthening data security and elevating customer experiences.
In this post, we’ll clarify the tokenization payment meaning, how it works, and how it benefits businesses. We also present some major types of payment tokens and their practical applications. Let’s discover!
What is payment tokenization?
Payment tokenization replaces a customer’s card number (PAN) with a unique token stored securely in a token vault.
In other words, no real cardholder information is used or stored during the transaction, which ensures payment security.
Even if accessed by hackers or fraudsters, these tokens are of no use as they contain no actual card details. As a result, payment data tokenization enables safe and secure payment processing with minimized risks of data breaches and fraud.
What is an example of payment tokenization?
For example, when a customer swipes their card at the POS terminals to complete a purchase, the credit card number 1182 3784 2735 0123 will be replaced with the token 3@K* @#5% BL+& *011, making the transaction safe and secure. The real payment details will be unexposed and stored in a highly secure token vault.
Tokenization vs. encryption
Both tokenization and end-to-end encryption are security techniques used to safeguard sensitive information from security risks and attacks. However, their approaches to data protection are different.
- Tokenization replaces confidential data with random, unrelated tokens. These tokens are irreversible, which means it’s impossible to extract original sensitive information without accessing the token vault. Therefore, payment processing tokenization can limit the exposure of critical data to malicious outsiders while maintaining compliance with data security standards such as PCI DSS.
- Encryption transforms sensitive card details into ciphertext, an unreadable format of data, by employing an encryption algorithm and a key. This indicates that only the people who know the encryption algorithm and the key can decode the encrypted data to find the original information.
Tokenization | Encryption | |
How it works | Substitute sensitive card details with a randomly generated string of characters called a token | Convert the readable form of payment information into an unreadable format |
Reversibility | No | Yes |
Data format | Keep the original data structure | Change the original data format |
Security |
|
|
Best for | Processes or environments where original data is referenced, not revealed | Processes or environments where data must be handled in its original form |
How does payment tokenization work?
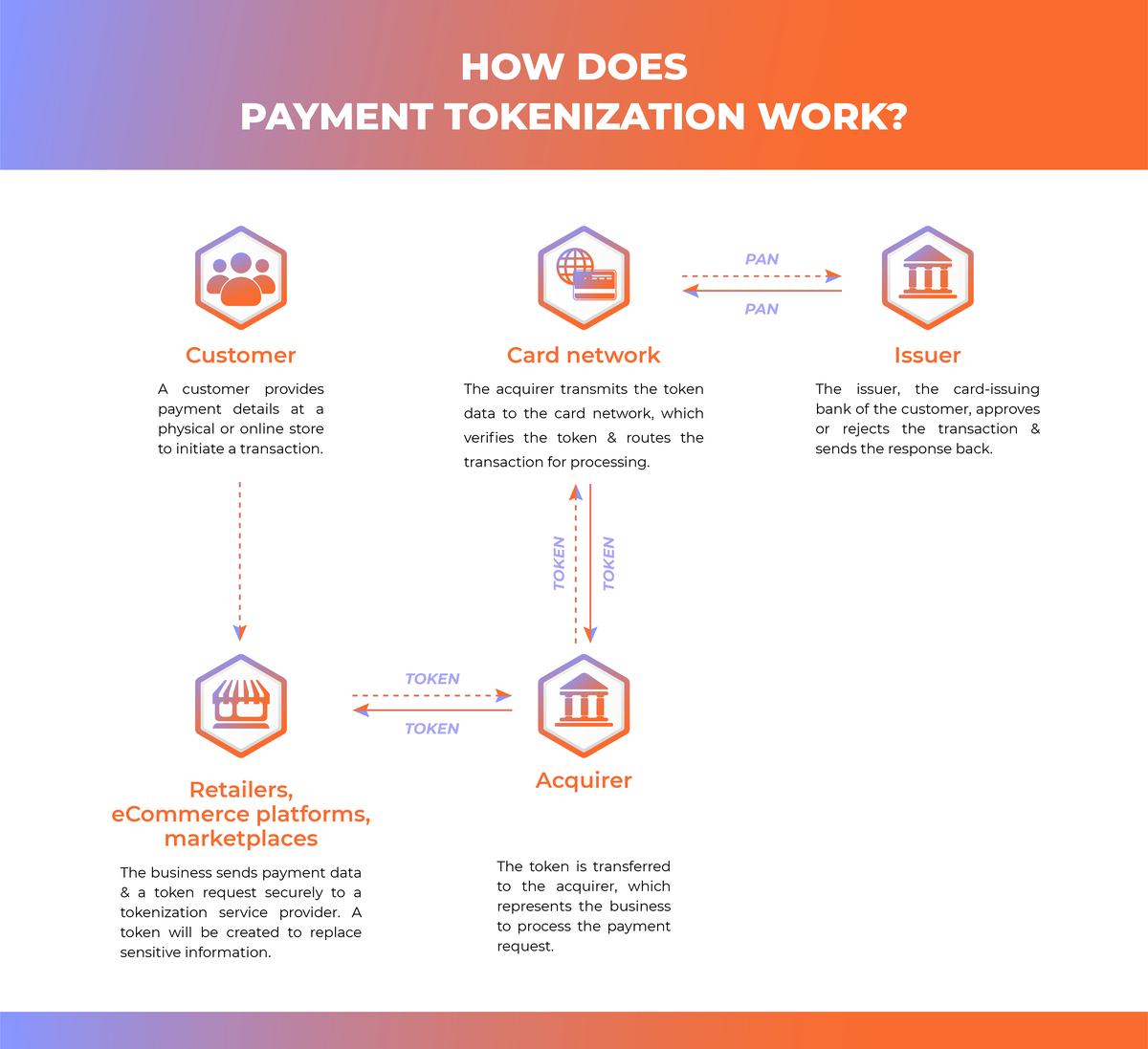
Tokenization helps protect your customers’ payment information, whether they make purchases online or in brick-and-mortar stores. Below is how payment tokenization works in reality.
- Collect data: A customer enters their payment credentials online or taps or swipes their card to start the transaction.
- Request tokens: After that, the merchant’s payment system sends the payment details and a token request to a payment processor or a 3rd-party token service vendor. Otherwise, merchants can automatically create tokens in-house using tokenization payment technology (software or hardware).
- Create tokens: The token service provider will generate a token to replace the original payment details using algorithms, encryption, and storage methods. The token is meaningless outside the payment system, as it’s irrelevant to the actual card information.
- Store tokens: The tokens will be forwarded to and stored in the merchant’s system in place of the actual payment data. Meanwhile, the real data is securely saved in token vaults owned by tokenization vendors, a secure environment strictly protected from unauthorized access.
- Use tokens: For future transactions, the business transfers the tokens to the token creator or payment processor. The tokenization provider will then search the token vault for the matching original cardholder data to allow tokenization payment processing. With tokenized transactions, the business has no access to the raw payment data, thus keeping it safe from fraudsters or hackers.
- Reuse tokens: Businesses can use a token multiple times without requiring the repeated collection of the original cardholder data, which is extremely beneficial to recurring transactions.
What are the different types of tokenization?
Payment tokens are classified according to token providers with several major types as below.
- Universal tokens: This token type works across multiple processors and networks, suitable for multi-channel environments. Besides payments, these tokens can also supplant other sensitive information. Consequently, many businesses choose universal tokens to shield different kinds of data from security threats.
- Acquirer tokens: Acquirer tokens are issued by acquiring banks and used only within their systems. When the card information is submitted for processing, acquirers return the tokens to merchants in response to the transaction requests.
- Issuer tokens: Card issuers generate their own tokens to use for digital wallets or mobile payment apps like Google Pay or Apple Pay. Issuer tokens are in the ownership of the card-issuing banks.
- Network tokens: Besides acquirers and issuers, card networks like Mastercard, Visa, and American Express also distribute their tokens, which can be used within a particular card network’s systems. To put it more clearly, payment network tokenization replaces payment details for specific card-merchant pairs only.
- Payment processor tokens: Proprietary tokens issued by certain payment service providers operate exclusively within their ecosystems. This ensures secure transactions but can limit interoperability with other payment processors.
- Merchant tokens: Payment tokenization service providers create merchant tokens for specific merchants after customers present their cards for transaction processing. Merchants own these tokens and can integrate them into their systems or combine them with other tokens as part of their payment operations.
7 benefits of payment tokenization
Merchants of all different sizes across industries can enjoy considerable tokenization benefits.
- Enhance payment security: Tokenization protects payment card data transit by substituting all raw payment details with a unique token with no inherent meaning. In this way, vulnerable payment data isn’t transmitted or stored during the transaction, thus mitigating the likelihood of data breaches, data leaks, or unauthorized access.
For example, a credit card number 7584 1982 7433 0937 can be displaced by the token A6K3 @#5% UF+-*0110. The token safeguards the real payment data during transmission and becomes worthless for bad actors.
- Prevent fraud: Tokens are irreversible and irrelevant to the actual payment data. Therefore, even when hackers or fraudsters have access to the tokens, they can’t retrieve any original information from them, thus improving payment fraud prevention.
- Guarantee PCI DSS compliance: Tokenizing customers’ sensitive cardholder information minimizes data security risks and helps businesses comply with industry standards. As merchants handle and store less payment data, they’re liable for a smaller PCI compliance scope. Besides lowering merchants’ costs to meet PCI standards, tokenized payments also help decrease potential damage related to data breaches, such as penalties or negative effects on brand reputation.
- Ease recurring transactions: Payment processing tokenization allows businesses to securely save tokens for future transactions. As a consequence, merchants can streamline recurring billing payment processing, eliminate the need for repetitive information gathering, and reduce the risks associated with managing sensitive payment data.
For example, if you provide a subscription-based service, your customers can register for recurring payments. By doing this, you can automatically rebill them for your services without asking for cardholder details again.
- Improve customer experience: Card-on-file tokenization enables your returning customers to enjoy a smoother and faster checkout experience, as businesses can reuse their saved tokens to accelerate the payment processing. In addition, payment card tokenization helps protect your customers’ card details from security threats, thereby winning their trust and loyalty.
For instance, a customer’s payment information will be stored in the form of tokens after they make their first transaction on your site. When they come back and buy another item, they won’t have to fill in the payment form anymore. Instead, they can finish the sale promptly with one-click payment.
- Facilitate omnichannel experience: With secure payment tokenization, merchants can manage customers’ payment details across channels. Therefore, customers can easily complete a sale on whichever channel they find most convenient, whether it’s online, mobile, or in-store.
Let’s take an example. When a customer pays for their first purchase at your physical store by swiping their card at the payment terminal, a token will be generated and stored. When the customer orders another product online later, this token will be reused without requiring them to enter the details, providing the customer with a secure cross-channel checkout experience. - Support multiple payment methods: Adopting tokenization enables merchants to securely accept a wide range of payment methods, including digital wallets, contactless payments, and mobile payments. As tokens can be applied to new payment technologies to safeguard transactions, businesses can employ the latest payment methods to satisfy customers’ demands and maintain payment security.
Contactless payment and digital wallet tokenization open up new ways to make payments. Businesses can now allow their customers to pay via wallet apps like Google Pay or Apple Pay, which is fast, convenient, and safe.
Practical applications of payment tokenization
Tokenization in payments can be advantageous to various business models, from eCommerce shops to physical storefronts. We list some of the common payment tokenization use cases for your reference.
- Brick-and-mortar retailers: Merchants can implement tokenization at their POS systems to handle card-present transactions in-store securely. Tokenization stores cardholder data outside the POS, keeping it safe from security threats and reducing the liability of businesses when a security incident happens. Moreover, retailers can support a wide array of payment methods, including mobile payments and digital wallets, and offer customers a seamless omnichannel checkout experience.
To enable tokenization payment processing for physical stores, your POS system should work properly with certain token providers.
For example, Magestore POS is a payment agnostic POS software, so the POS can integrate with numerous payment processors with built-in tokenization services, such as Square, Stripe, Authorize.net, and Adyen, to secure in-store payments. - eCommerce websites: Payment data tokenization enhances security for online transactions by replacing vulnerable card data with a nonsensitive token. Consequently, both merchants and shoppers don’t need to worry about cyberattacks or data breaches, as no actual information is revealed during the transaction. Reusable tokens also help simplify payment processing for repeat customers by enabling one-click checkout, letting customers proceed with their purchases without re-entering their card details.
- Subscription-based businesses: Implementing card payment tokenization frees these businesses from storing and managing sensitive cardholder data for ongoing transactions. Instead of storing or repeatedly requesting card information, they just need to use tokens to process recurring payments. Even if customers change their subscription plans, like upgrades or cancellations, the business can easily handle these updates by using the same tokens. This provides customers with a more seamless customer experience, thereby increasing their long-term loyalty.
- Mobile wallets: Mobile users can download wallet apps like Google Pay or Apple Pay and add their card information. After that, randomized tokens linked to the cards will be created to replace the original payment details. Customers can then use these tokens to make payments on their mobile devices. In this case, mobile payment tokenization not only protects users’ payment data during the transaction but also speeds up payment processing.
- Platforms and marketplaces: Tokenization in payment processing fosters easy, secure, and seamless payments between multiple parties in a platform or marketplace. Using tokens rather than raw card information limits data exposure, thus securing all payments from all users and preventing unauthorized access. Additionally, tokenization helps platforms and marketplaces streamline payouts to relevant parties like sellers, as they can reuse tokens for recurring payments. If your business enters new markets, tokenization architecture eases the integration of new payment methods to accommodate new payment needs.
Wrapping up
Payment tokenization shields sensitive cardholder data from fraudulent actors by turning it into a randomized, unique, and irreversible token for transaction processing. If these tokens are compromised, there’s no way to recover the original payment data from them. As a result, this security technique helps mitigate the risks of exposing customers’ payment details, thus enhancing data security while reducing the PCI liability of merchants. Businesses can also reuse tokens to provide their customers with a secure and smooth checkout experience across channels.
There are different kinds of tokens, including acquirer tokens, issuer tokens, and network tokens. Tokenization in payment processing can be utilized in numerous business use cases, from marketplaces to eCommerce platforms, like Magento, Shopify. To provide customers with diverse yet secure payment experiences at your brick-and-mortar store, you need a POS system that can work with different payment processors that come with built-in tokenization services like Magestore POS.
To build a secure POS system for your business, let’s talk with our experts.
FAQs about payment tokenization
1. What is tokenization in payment processing?
Payment processing tokenization refers to the substitution of sensitive cardholder details with a token, a randomly generated sequence of characters and numbers, used for payment processing.
2. Are payment tokens reversible?
No, the tokens are irreversible. Once the payment data is tokenized, it’s impossible to transform it back into the original format.
3. How do single-use tokens differ from multi-use tokens?
Merchants use single-use tokens for only one transaction, whereas multi-use tokens can be reused for various transactions.
4. How does tokenization work for online card-on-file payment?
After a customer provides their card details to complete their first transaction at a business, a token linked to the card will be created and saved for future transactions.
5. How does tokenization enhance payment security?
Payment tokenization solutions employ a unique token to secure sensitive cardholder details. This token bears no relevance to the actual card information, so it can’t be exploited to get the real data. During the transaction, it’s the token, not the customers’ original card details, that is transferred and used. Therefore, customers and merchants can rest assured that there is no data leakage or breaches, even when fraudsters can access the token.